
I am a third-year EECS PhD student at MIT advised by professors Leslie Kaelbling and Tomás Lozano-Pérez. I am part of the Learning and Intelligent Systems (LIS) Group, and part of the broader CSAIL Embodied Intelligence (EI) Group. I am broadly interested in task-aware perception and compositional reasoning for embodied agents, enabling robots to achieve open-ended tasks in dynamic environments.
Previously, I was a robotics perception intern at Autodesk, where I worked on fast and adaptable robotic perception and foundation models for multi-part automated robot assembly. I was also a visiting researcher at REAL at Université de Montréal associated with Mila advised by Prof. Liam Paull, an intern at Microsoft Research India, working on problems in the areas of Education, Skilling, and Healthcare, and a MITACS research intern at the University of Calgary, where I worked on characterizing and localizing an audio noise nuisance called the Ranchlands Hum, advised by Prof. Mike Smith.
I completed my Masters by research from IIIT Hyderabad in Computer Science and Engineering, advised by professors C V Jawahar and Vinay Namboodiri in the computer vision (CVIT) lab and by professors Madhava Krishna and Srinath Sridhar (Brown University) in the robotics (RRC) lab. I completed my Bachelors from PES University (formerly PESIT) Bangalore in Computer Science and Engineering.
Research Interests: My research focuses on developing algorithms that enable embodied agents to dynamically perceive and reason about the world in order to achieve open-ended tasks. Specifically, I study task-aware perception and compositional reasoning, enabling robots to dynamically construct task-relevant representations by combining multimodal perception with planning and policy learning methods. I also study novel and efficient ways of integrating representation learning with robot policy learning to improve generalization (across pose and viewpoint variations), sample efficiency (requiring fewer demonstrations), and data-collection efficiency (learning from human demonstrations and leveraging world models as a proxy for data generation).
Publications
|
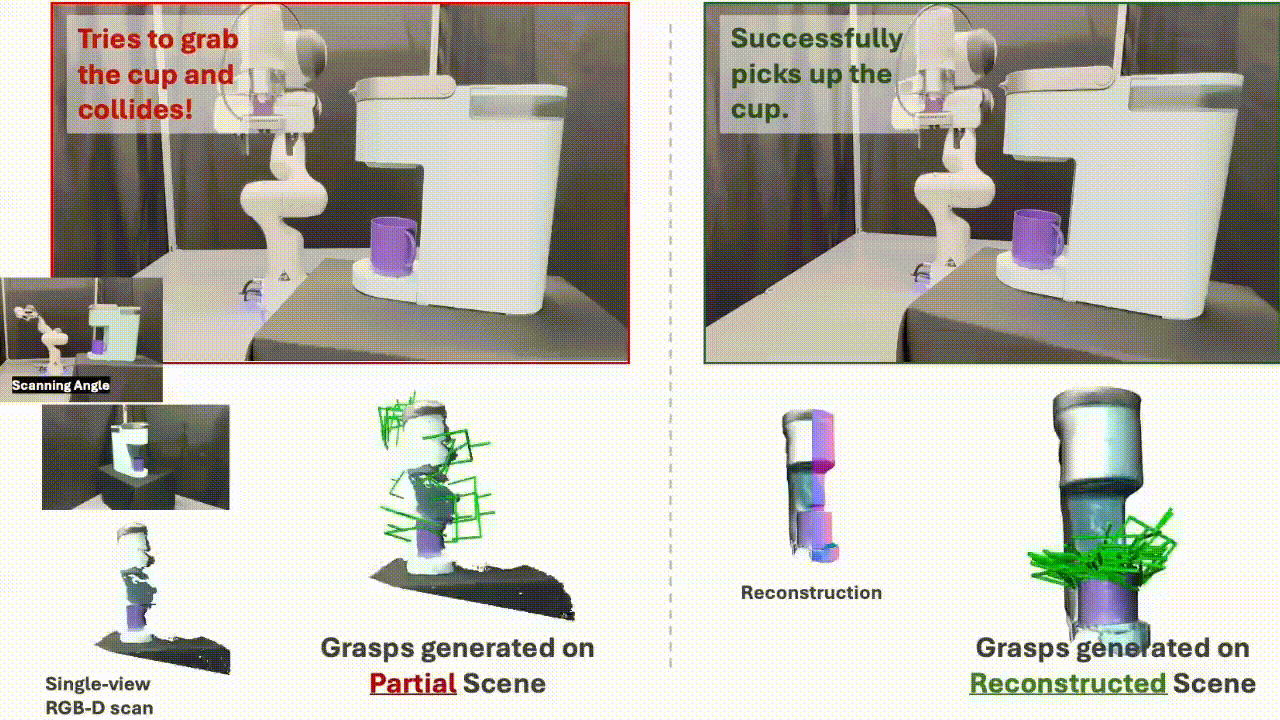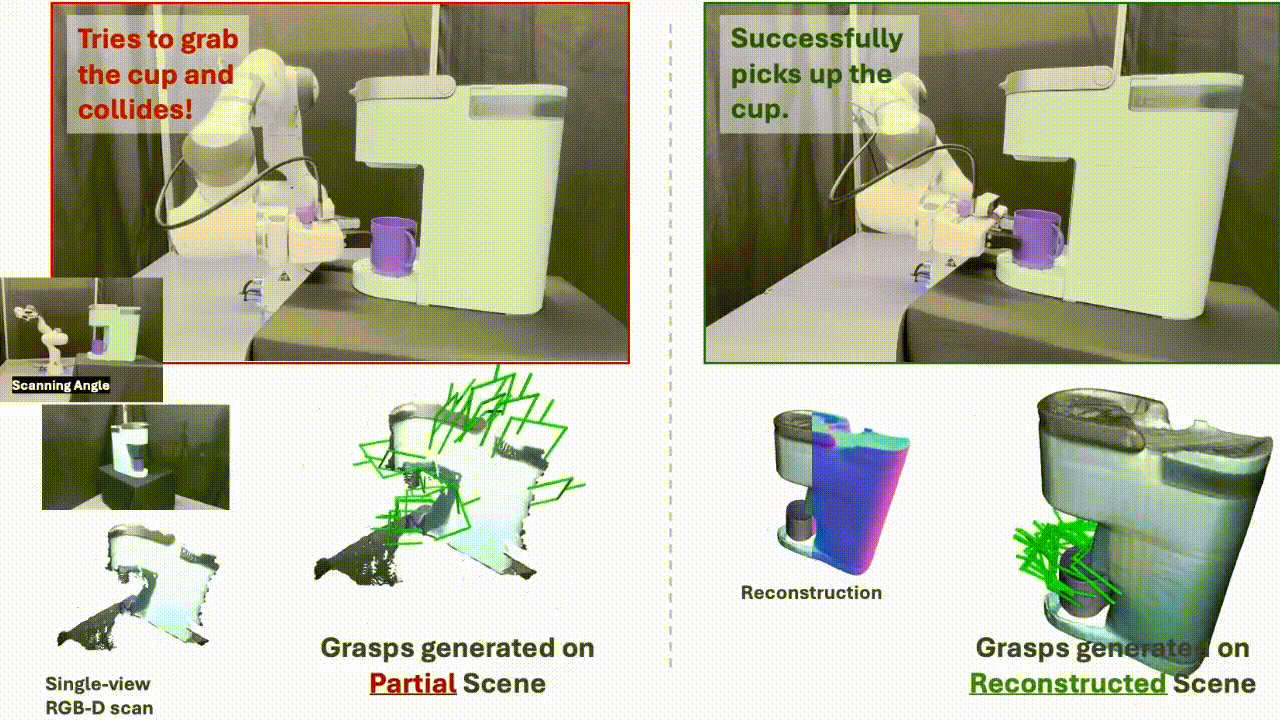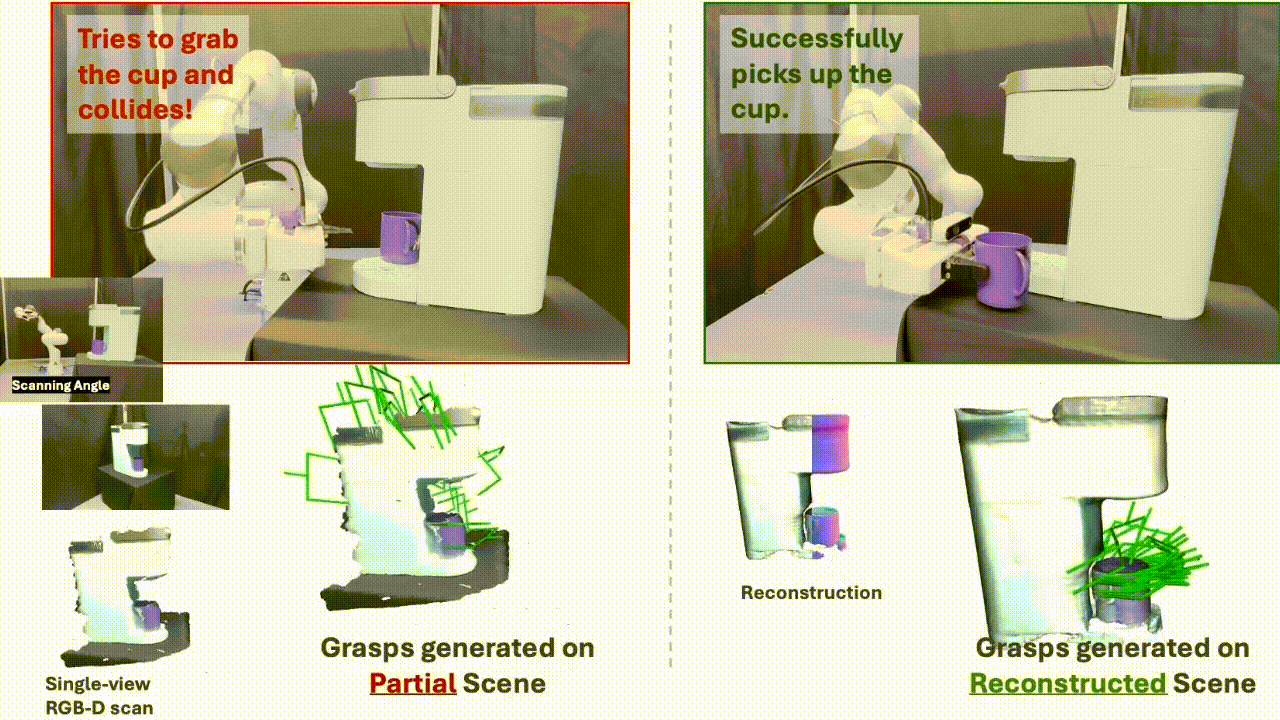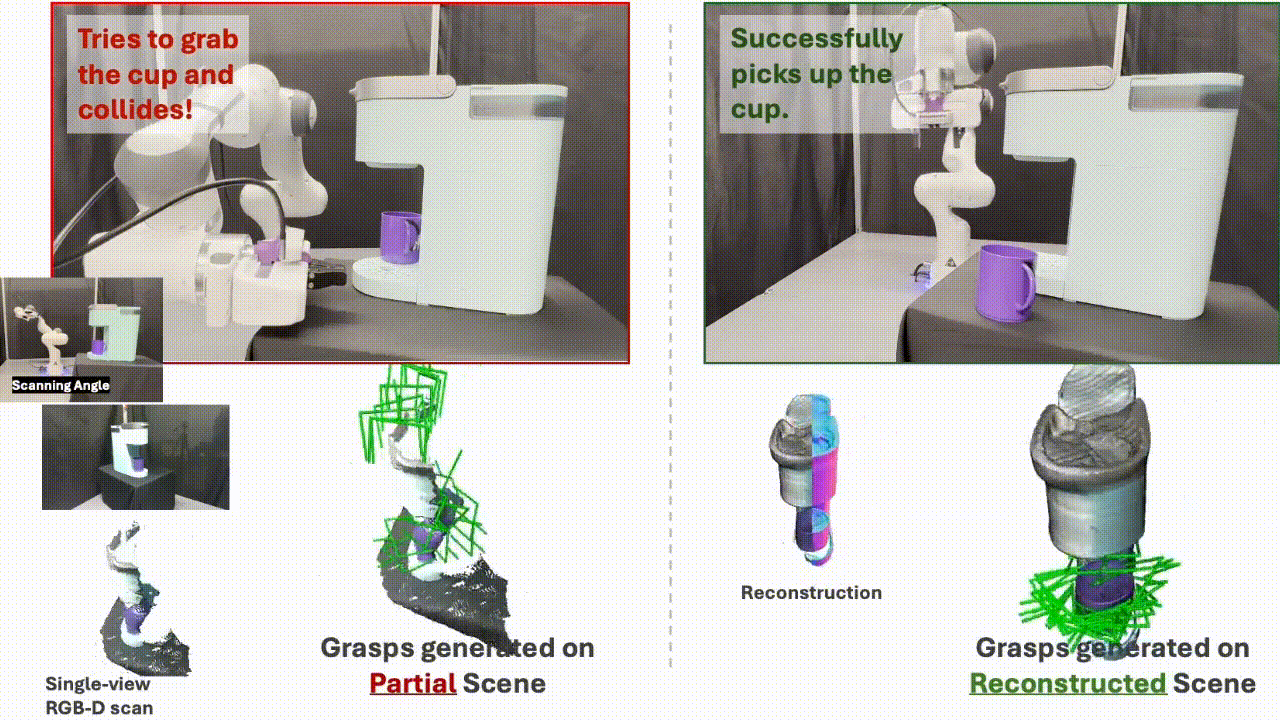
SceneComplete: Open-World 3D Scene Completion in Cluttered Real World Environments for Robot ManipulationPaper / Project Page / Code / Video We propose SceneComplete, a method for open-world 3D scene completion in cluttered real-world environments to improve robot manipulation. Our approach enables robots to reason about occluded and unseen parts of objects and scenes, enhancing their ability to plan and execute manipulation tasks in complex, real-world settings. |

|
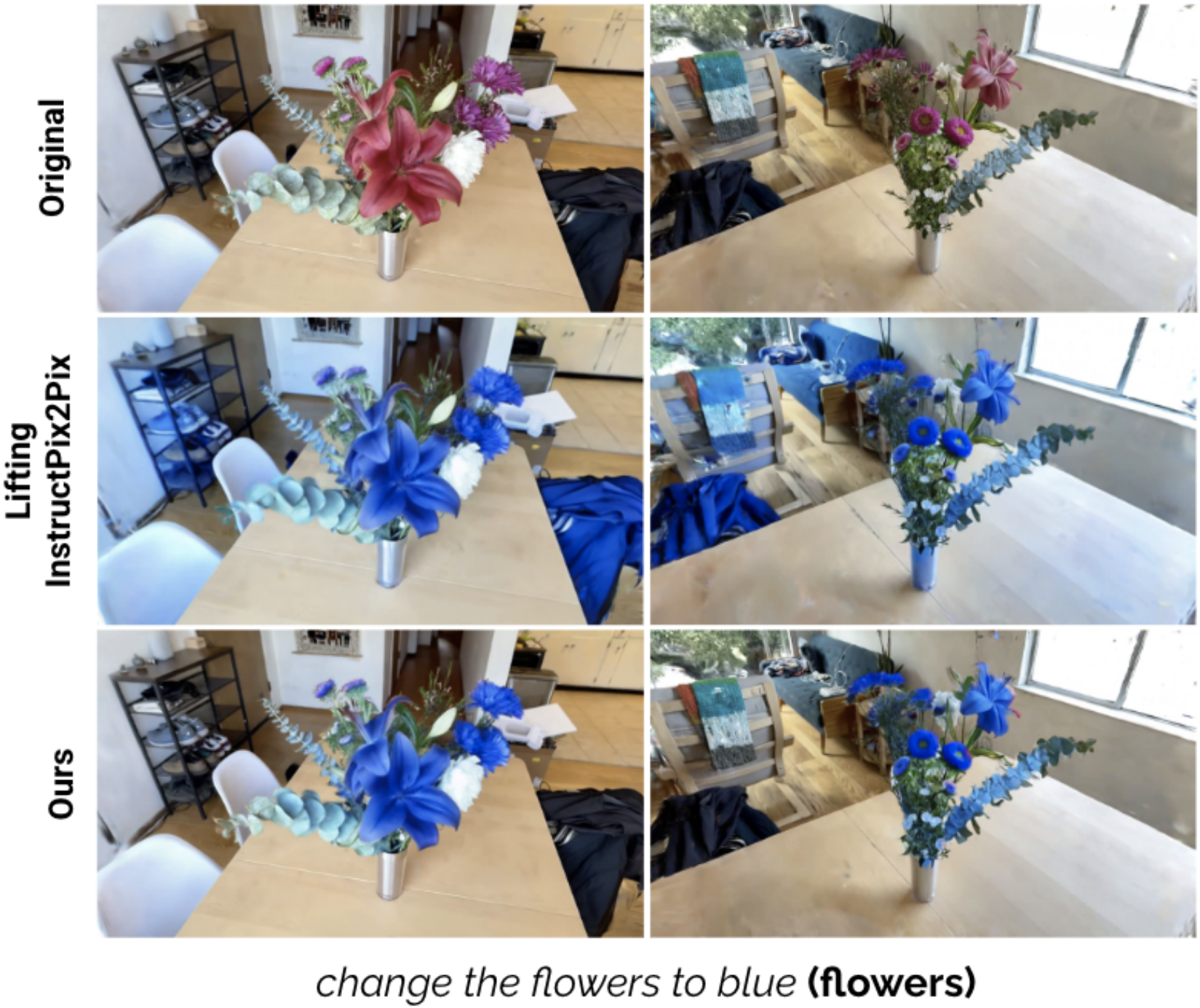
Vector Quantized Feature Fields for Fast 3D Semantic LiftingWe propose Vector-Quantized Feature Fields, a method for efficient semantic lifting that enables lightweight on-demand retrieval of pixel-aligned relevance masks. Our approach generalizes lifting to semantic lifting by incorporating per-view masks derived from multiscale pixel-aligned feature maps. We demonstrate its effectiveness on complex indoor and outdoor scenes, enabling text-driven localized scene editing and significantly improving the efficiency of embodied question answering. |
|
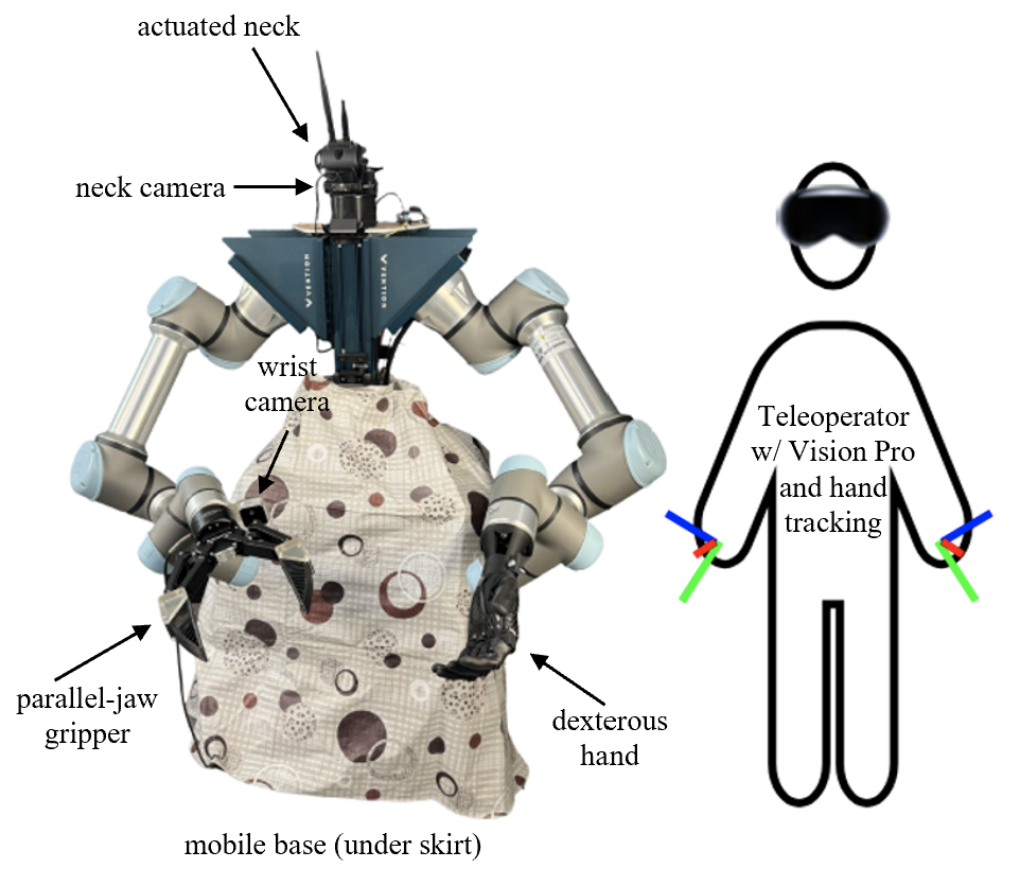
Learning to look around: Enhancing teleoperation and learning with a human-like actuated neckCoRL 2024 Workshop WCBM (Spotlight) We introduce a teleoperation system with a 5-DOF actuated neck that replicates natural human head movements, providing operators with a more intuitive view of the environment. The system improves task performance, reduces cognitive load, and facilitates complex whole-body manipulation across seven challenging teleoperation tasks. We demonstrate how the actuated neck supports better spatial awareness in training autonomous policies through imitation learning, reducing distribution shift compared to static wide-angle cameras. |

|
ConceptGraphs: Open-Vocabulary 3D Scene Graphs for Perception and Planning,Paper / Project Page / Code / Video We propose ConceptGraphs, an open-vocabulary graph-structured representations for 3D scenes, built by leveraging 2D foundation models and fusing their output to 3D by multiview association. The resulting representations generalize to novel semantic classes, without the need to collect large 3D datasets or finetune models. The utility of this representation is demonstrated through downstream robotic planning tasks. |
|
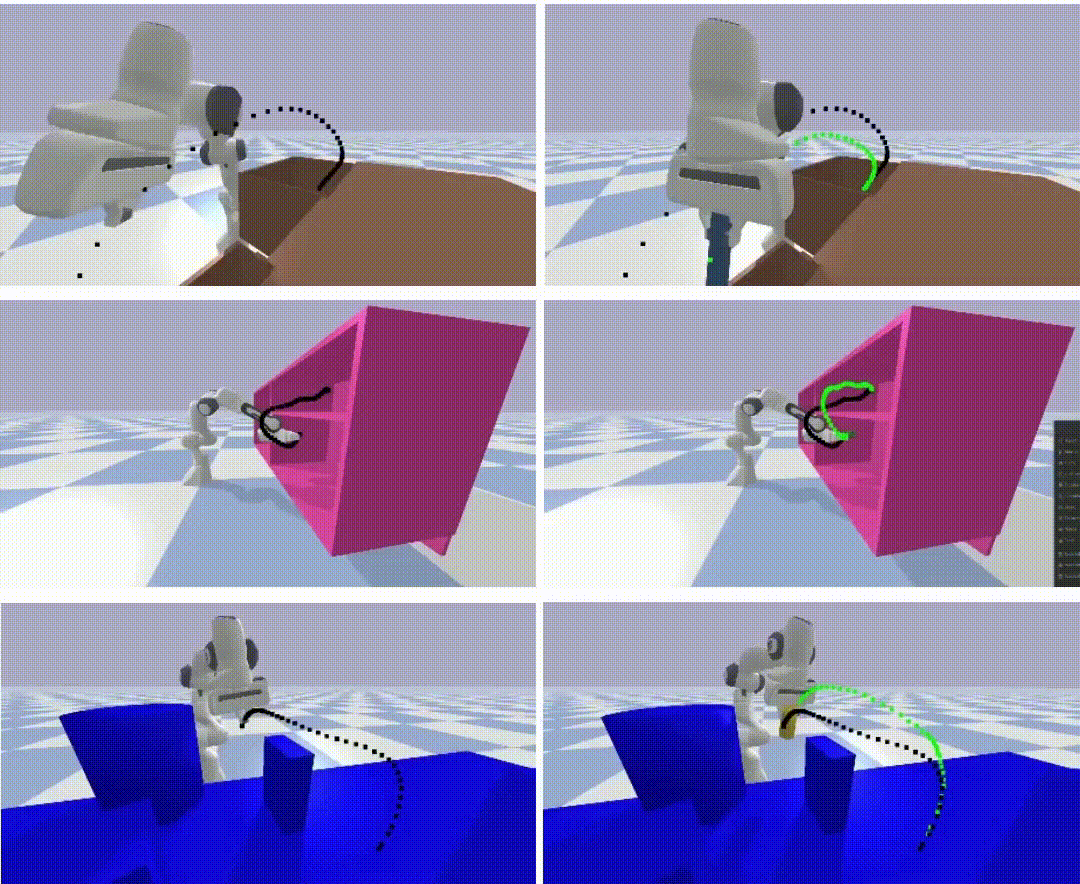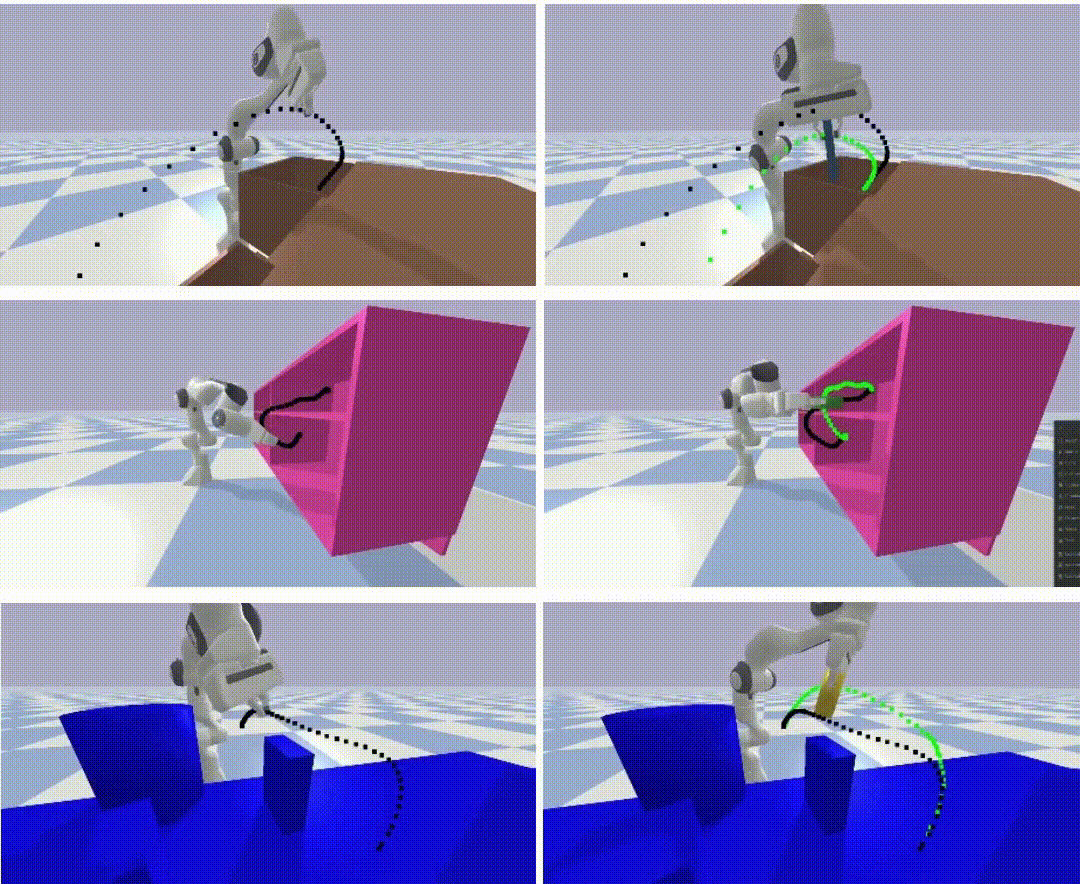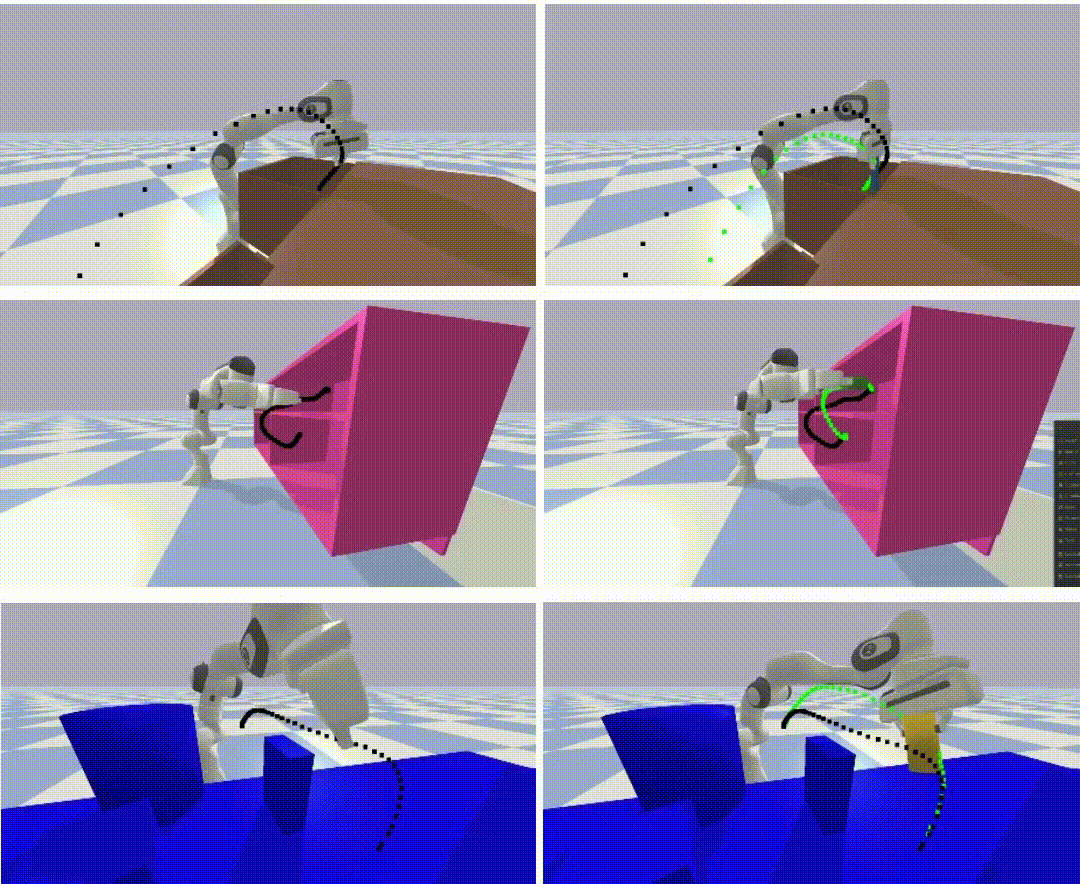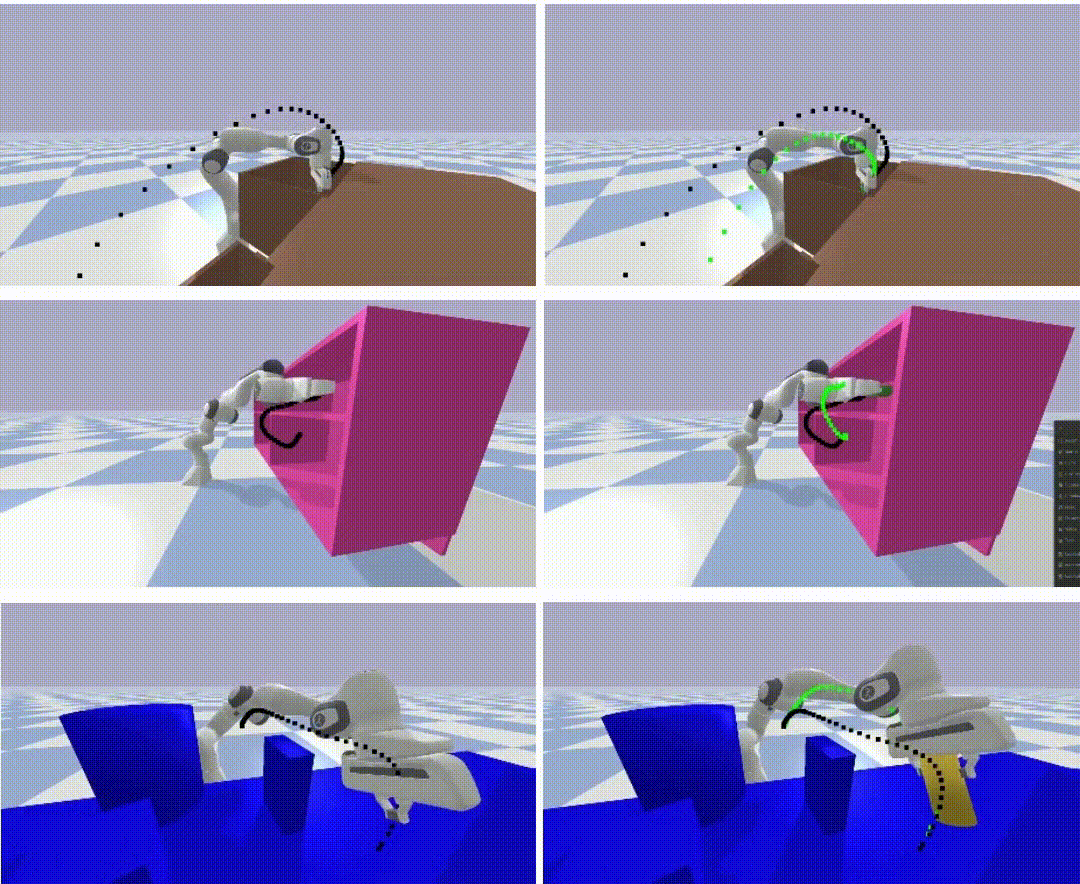
EDMP: Ensemble-of-costs-guided Diffusion for Motion Planning,Paper / Project Page / Code / Video We propose EDMP for motion planning, that combines the strengths of classical motion planning (offering remarkable adaptability) and deep-learning-based motion planning (prior understanding over diverse valid trajectories). Our diffusion-based network is trained on a set of diverse kinematically valid trajectories. For any new scene at the time of inference, we compute scene-specific costs such as "collision cost" and guide the generation of valid trajectories that satisfy scene-specific constraints. |
|
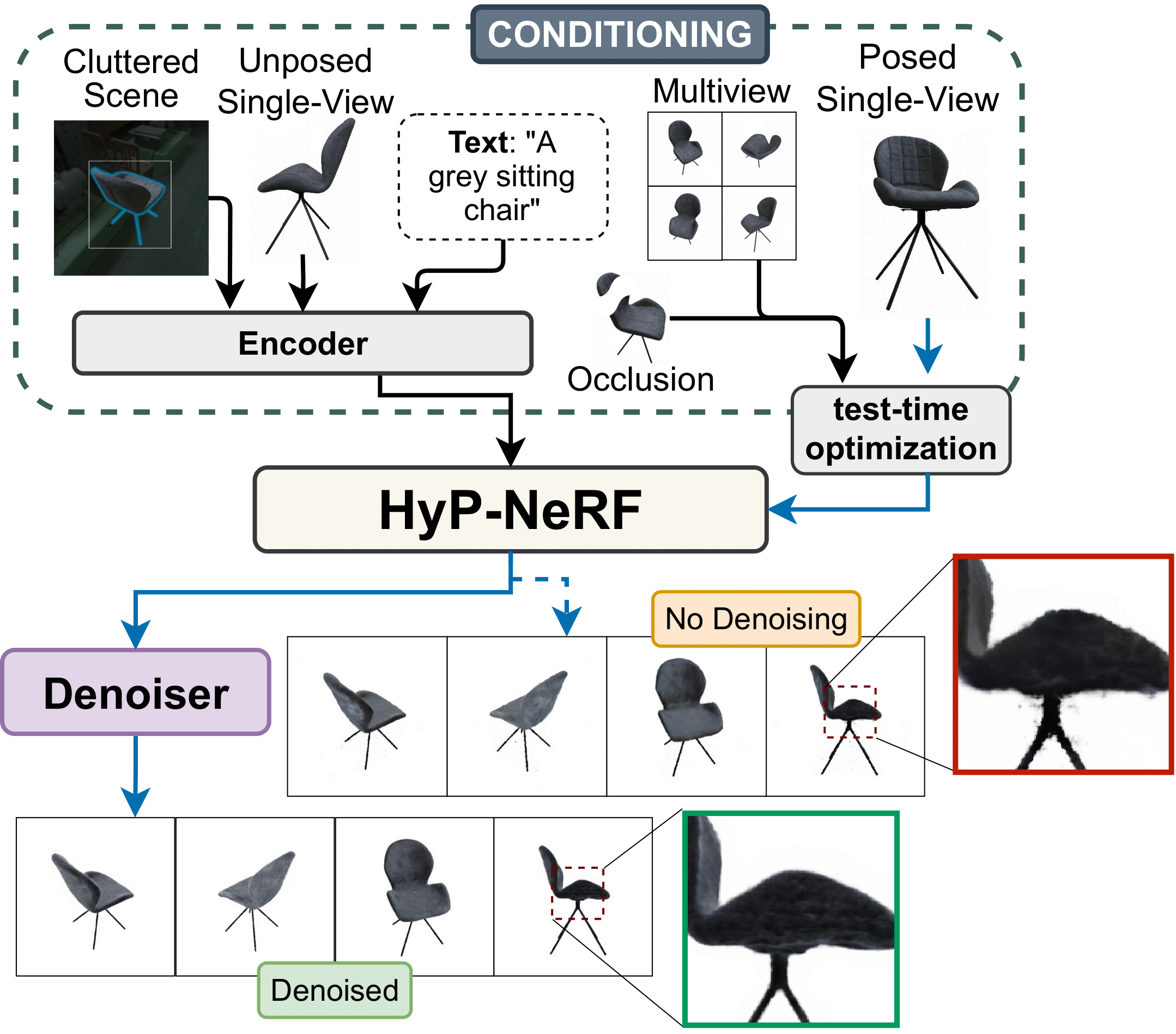
HyP-NeRF: Learning Improved NeRF Priors using a HyperNetworkWe propose HyP-NeRF, a latent conditioning method for learning generalizable category-level NeRF priors using hypernetworks. We use hypernetworks to estimate both the weights and the multi-resolution hash encodings resulting in significant quality gains. To further improve quality, we incorporate a denoise and finetune strategy that denoises images rendered from NeRFs estimated by the hypernetwork and finetunes it while retaining multiview consistency. |
|
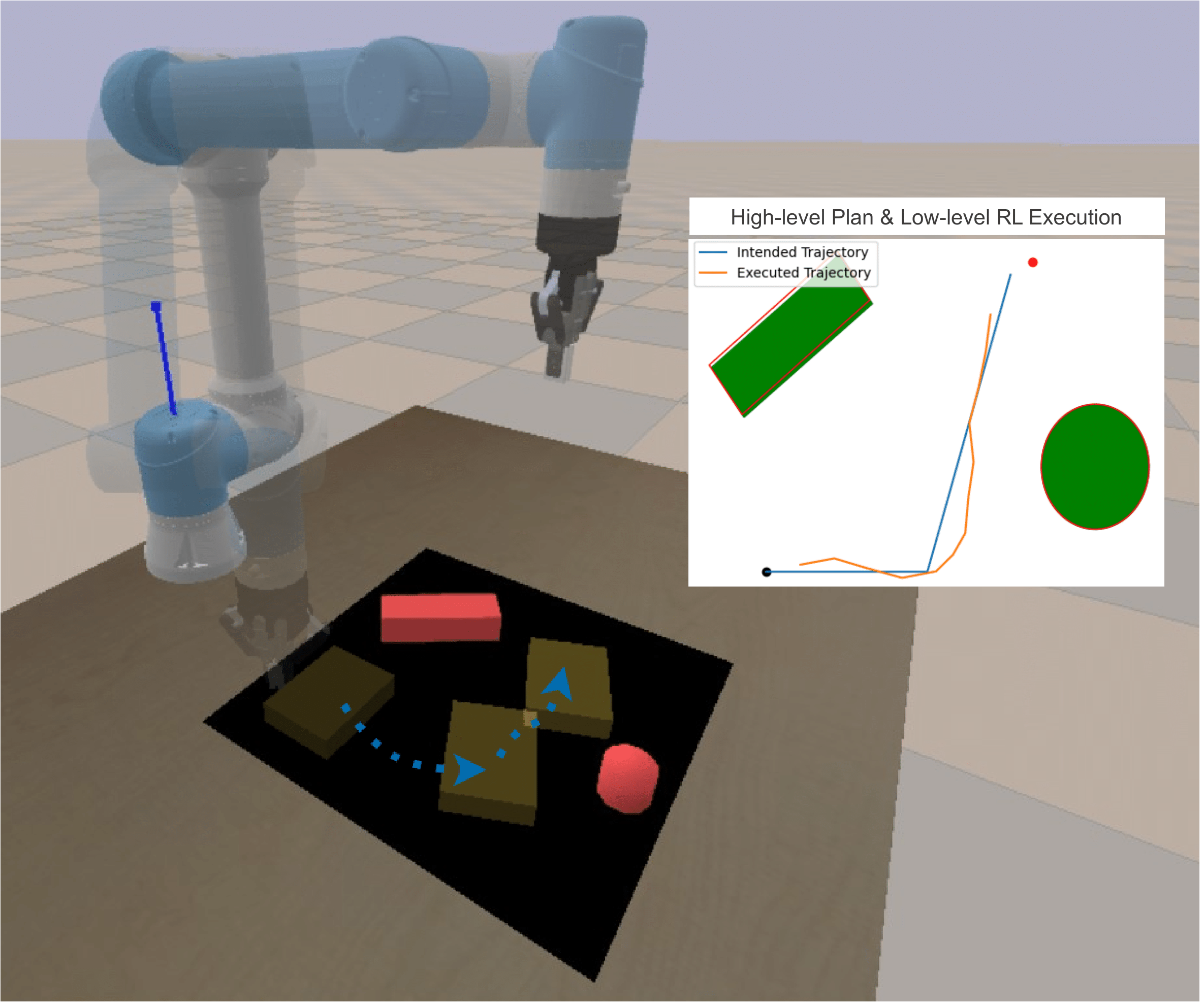
Disentangling Planning and Control for Non-prehensile Tabletop ManipulationWe propose a framework that disentangles planning and control for tabletop manipulation in unknown scenes using a pushing-by-striking method (without tactile feedback) by explicitly modeling the object dynamics. Our method consists of two components: an A* planner for path-planning and a low-level RL controller that models object dynamics. |
|
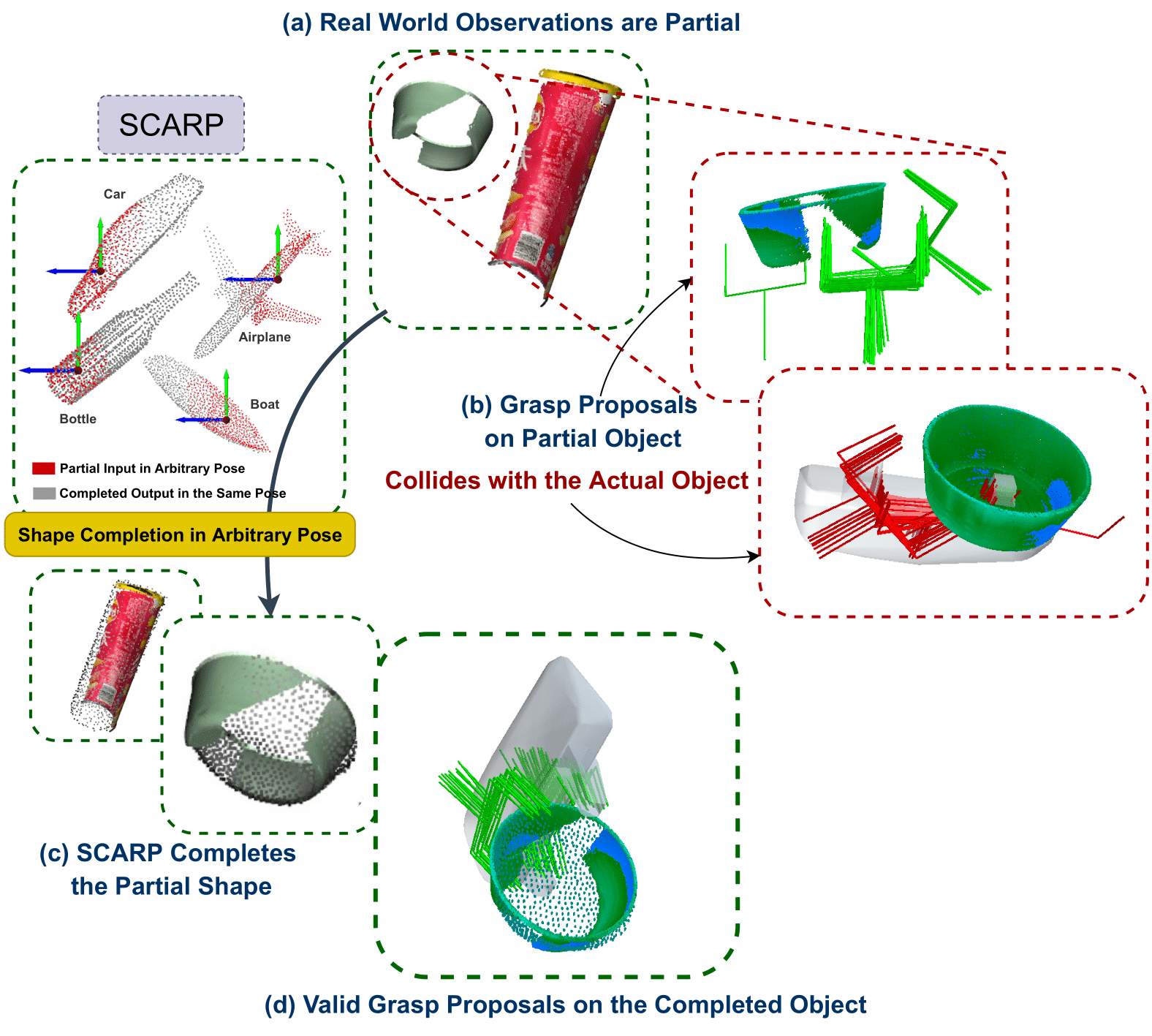
SCARP: 3D Shape Completion in ARbitrary Poses for Improved GraspingPaper / Project Page / Short Video / Code / Poster / Long Video We propose a mechanism for completing partial 3D shapes in arbitrary poses by learning a disentangled feature representation of pose and shape. We rely on learning rotationally equivariant pose features and geometric shape features by training a multi-tasking objective. SCARP improves the shape completion performance by 45% and grasp proposals by 71.2% over existing baselines. |
|
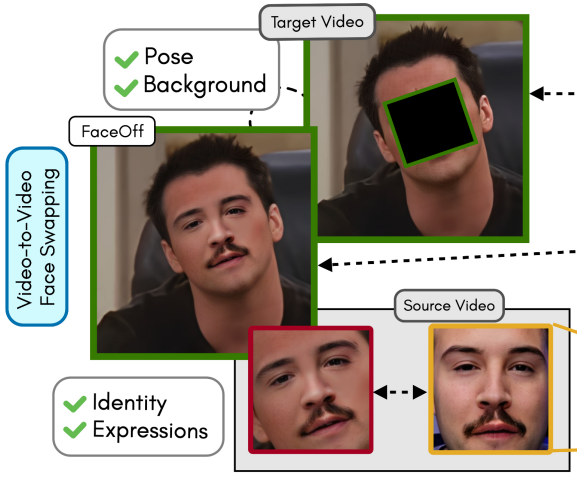
FaceOff: A Video-to-Video Face Swapping SystemPaper / Project Page / Video / Poster / Code / Supplementary We propose a novel direction of video-to-video (V2V) face-swapping that tackles a pressing challenge in the moviemaking industry: swapping the actor's face and expressions on the face of their body double. Existing face-swapping methods preserve only the identity of the source face without swapping the expressions. In FaceOff, we swap the source's facial expressions along with the identity on the target's background and pose. |
|
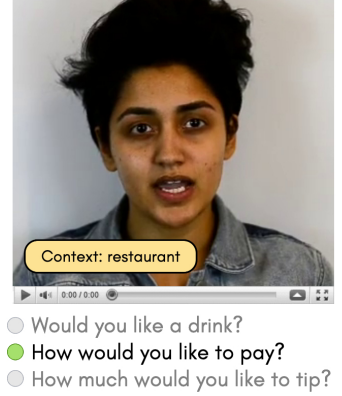
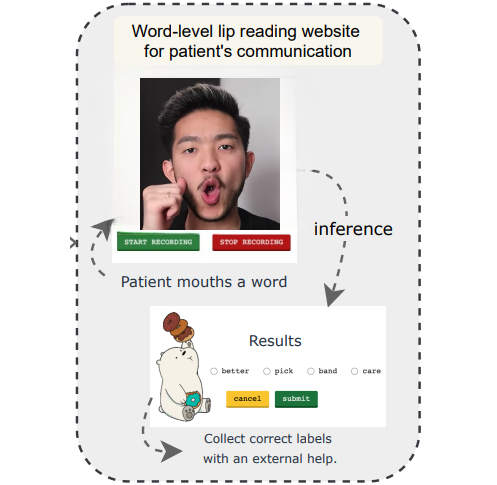
Towards MOOCs for Lipreading: Using Synthetic Talking Heads to Train Humans in Lipreading at ScalePaper / Project Page / Video / Poster / Supplementary Hard-of-hearing people rely on lipreading the mouth movements of the speaker to understand the spoken content. In this work, we developed computer vision techniques and built upon existing AI models, such as TTS and talking-face generation, to generate synthetic lipreading training content in any language. |
|
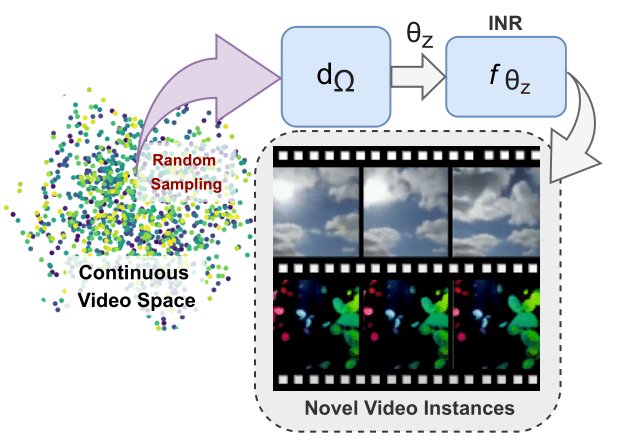
INR-V: A Continuous Representation Space for Video-based Generative TasksPaper / OpenReview / Project Page / Video / Code Inspired by the recent works on parameterizing 3D shapes and scenes as Implicit Neural Representations (INRs), we encode videos as INRs. We train a hypernetwork to learn a prior over these INR functions and propose two techniques, i) Progressive Training and ii) Video-CLIP Regularization to stabilize hypernetwork training. INR-V shows remarkable performance on several video-generative tasks on many benchmark datasets. |
|
Approaches and Challenges in Robotic Perception for Table-top Rearrangement and Planning3rd in ICRA 2022 Open Cloud Table Organization Challenge Paper / Competition / Video / Slides / Code / News1 / News2 In this challenge, we proposed an end-to-end pipeline in ROS incorporating the perception and planning stacks to manipulate objects from their initial configuration to a desired target configuration on a tabletop scene using a two-finger manipulator. The pipeline involves the following steps - (1) 3D scene registration, (2) Object pose estimation, (3) Grasp generation, (4) Task Planning, and (5) Motion Planning. |
|
Personalized One-Shot Lipreading for an ALS PatientWe tackled the challenge of lipreading medical patients in a one-shot setting. There were two primary issues in training existing lipreading models - i) lipreading datasets had people suffering from no disabilities, ii) lipreading datasets lacked medical words. We devised a variational encoder-based domain adaptation technique to adapt models trained on large amounts of synthetic data to enable lipreading with one-shot real examples. |
|
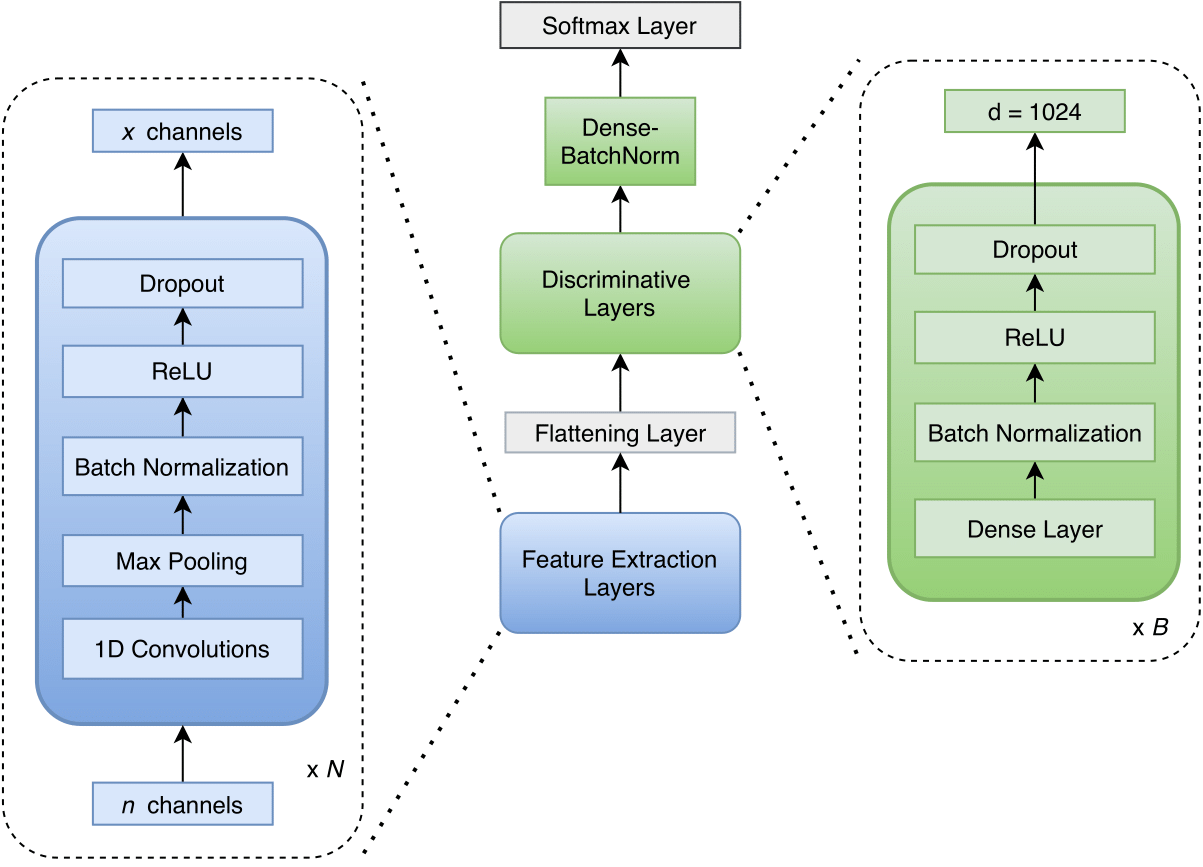
REED: An Approach Towards Quickly Bootstrapping Multilingual Acoustic ModelsWe tackled the problem of building a multilingual acoustic model in a low-resource setting. We proposed a mechanism to bootstrap and validate the compatibility of multiple languages using CNNs operating directly on raw speech signals. Our method improves training and inference times by 4X and 7.4X, respectively, with comparable WERs against RNN-based baseline systems. |
News & Announcements
-
[Nov '23] Awarded NeurIPS 2023 Scholar Award (~$1700).
-
[Nov '23] Co-presented 2 papers at PRL, TGR, and LangRob workshops at CoRL2023 in Atlanta, Georgia.
-
[Sep '23] Hyp-NeRF accepted at NeurIPS 2023. See you in New Orleans, Louisiana.
-
[Sep '23] Joined Massachusetts Institute of Technology as a PhD student in EECS.
-
[Apr '23] I'll be joining MIT CSAIL as a PhD student this Fall. I will be a part of the Learning and Intelligent Systems (LIS) Group with professors Leslie Pack Kaelbling and Tomás Lozano-Pérez.
-
[Apr '23] Full page abstract on "Uncovering Biases Against Indian Artists" accepted at ICMPC17-APSCOM7 for a spoken presentation. Awarded a Travel Grant of ¥30,000 to attend the conference in Tokyo, Japan.
-
[Mar '23] Awarded a generous travel grant of $2250.00 by ICRA 2023 IEEE RAS Travel Grant Committee to attend the premier robotics conference in London, UK from 29th May to 2nd Jun.
-
[Mar '23] Invited for a talk at Columbia University - slide deck here. The talk was organized as part of my graduate visit days to Brown, Columbia, and MIT.
-
[Jan '23] 5 works on Implicit Video Parameterization, V2V Face-Swapping, MOOCs for Lipreading, 3D Shape Completion, and Synergistic Tabletop Manipulation presented at IIIT Hyderabad's RnD showcase.
-
[Jan '23] 1 paper accepted at ICRA 2023 on 3D Shape Completion in Arbitrary Poses. Featured as the "Publication of the Week" in "Weekly Robotics".
-
[Jan '23] Attending Google Reserach Week in Bangalore from 29th Jan to 31st Jan.
-
[Oct '22] Journal paper on representation space for video-based generative tasks accepted at TMLR 2022.
-
[Aug '22] Two papers on video face swapping and talking-face generation accepted at WACV 2023 round 1 (acceptance rate 21.6%).
-
[May '22] We were in the News (news1, news2) for winning 3rd place at the ICRA 2022 international robotics competition on tabletop rearrangement and planning. Awarded a grant of $1000.00.
[Oct '21] 1 paper accepted at BMVC on lipreading in a one-shot setting using domain adaptation.
-
[Mar '21] I will be joining IIIT Hyderabad as an MS by Research student.
-
[Nov '20] 1 paper accepted at SLT on building multilingual acoustic model for low-resource languages.
-
[Sep '17] Completed my Bachelor's degree from PES University in Computer Science. Received Academic Distinction Award for exceptional academic performance.
-
[Jan '16] I will be interning at the University of Calgary in Summer 2016 fully-funded through the MITACS Globalink Research Award.
[May '23] I'll be starting as a research intern at Mila - Quebec Artificial Intelligence Institute, Montreal with professors Liam Paull and Florian Shkurti. I will work on learning representations for 3D robotic manipulation.
Academic Services
-
Reviewer for ICRA 2025, CVPR 2025 (Outstanding Reviewer Award).
-
Reviewer for SIGGRAPH 2023, IROS 2023, ICLR 2023 workshops, ICRA 2023.
-
[Aug '22] Coordinator for the 6th CVIT Summer School on AI.
-
[Aug '22] Gave a talk on the challenges in tabletop rearrangement and planning at CVIT Summer School 2022.
-
[Feb '22] I will be taking month long tutorial sessions in machine learning for faculties across universities in India as part of the CSEDU-ML program conducted jointly by IIIT-H, IIT-H, and IIT-D.
-
[Aug '21] Coordinator for the 5th CVIT Summer School on AI and conducted tutorial sessions on self-supervised learning and multimodal learning.
Professional Achievements
-
[Aug '17] Winners at the VMWare Global Relay Opensource Borathon among all participating teams at VMWare.
-
[Mar '20] I was selected as one of the two individuals out of 6,000 employees at Microsoft India to undergo a video shoot for the company's campus hiring program. Available on YouTube.
-
[Mar '18] My work helped scale the Microsoft Community Training platform to its first 100K users. The work was covered by several media outlets ([1], [2], [3], [4]). I was awarded the "Delight your Customer" Award by Microsoft for my outstanding work.
-
[Feb '17] My work on building Microsoft Research India's flagship project Massively Empowered Classroom was deployed by Mauritius Institute of Education. It was inaugurated by MD MSR India and Minister of Tertiary Education, Mauritius and was covered by the press ([1], [2], [3]).
Forked and modified from Viraj Prabhu's adaptation of Pixyll theme